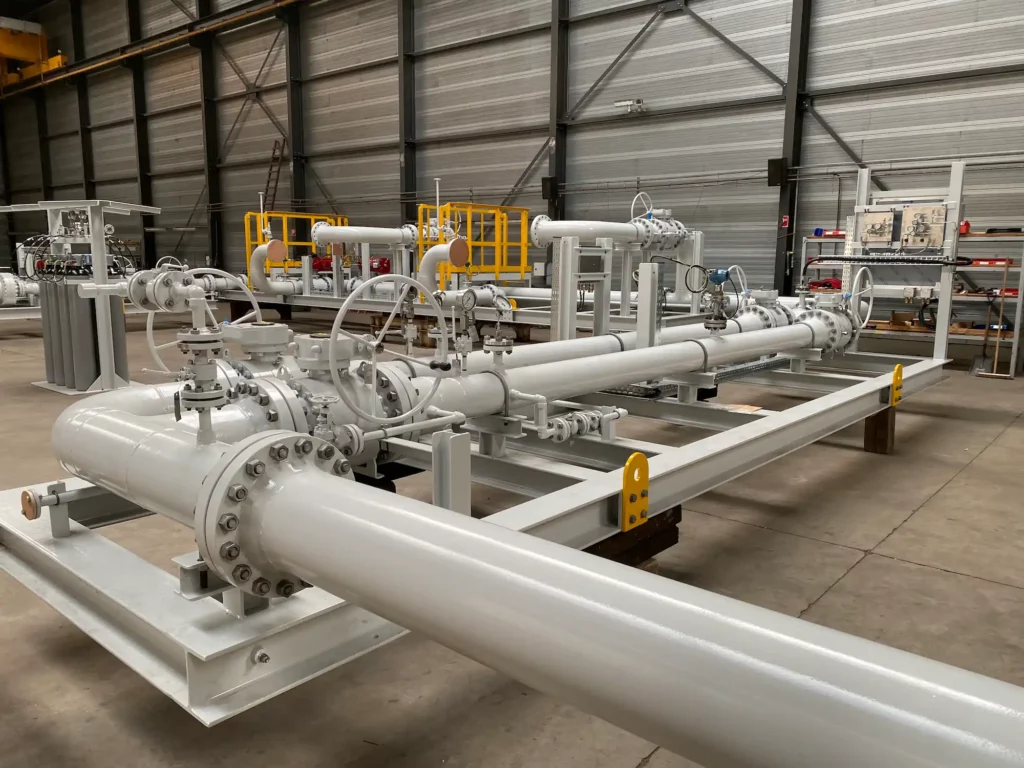
As the global energy sector transitions toward cleaner fuel sources, hydrogen has emerged as a critical energy carrier. However, transporting and storing hydrogen efficiently remains a significant challenge. This is where ammonia cracking units for hydrogen production play a vital role. These specialized process systems thermally decompose ammonia (NH₃) into hydrogen (H₂) and nitrogen (N₂) through catalytic cracking at elevated temperatures, typically between 700-1000 °C. By enabling the conversion of easily transportable ammonia back into high-purity hydrogen at the point of use, these units effectively bridge the gap between hydrogen production sites and end-user applications.
Understanding the ammonia cracking process
The fundamental chemistry behind ammonia cracking is straightforward yet powerful. The process reverses the well-known Haber-Bosch ammonia synthesis reaction through an endothermic decomposition: two molecules of ammonia break down into three molecules of hydrogen and one molecule of nitrogen. This reaction requires sustained heat input and occurs over specialized catalytic surfaces.
A complete ammonia cracking unit comprises several integrated process sections. The feed preparation stage receives liquid or gaseous ammonia, vaporizes it under controlled pressure conditions (typically 20-50 bar), and preheats it to reaction temperature. The heart of the system is the catalytic cracking reactor, where ammonia flows over nickel-based catalysts in tubular reactors or furnace-heated crackers. External heat sources-whether fuel-fired furnaces, electric heating elements, or integrated process heat-maintain the necessary temperature profile for complete conversion.
Heat recovery and gas purification
Efficient ammonia cracking units incorporate sophisticated heat integration systems. The hot cracked gas exits the reactor and passes through waste heat recovery equipment, where its thermal energy preheats incoming ammonia feed or generates process steam. This heat integration significantly improves overall thermal efficiency, with well-designed systems achieving efficiency rates exceeding 90%.
The raw cracked gas typically contains approximately 75% hydrogen and 25% nitrogen. For applications requiring high-purity hydrogen-such as fuel cells or sensitive industrial processes-the gas stream undergoes purification through Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) technology. PSA units remove nitrogen, residual ammonia, and trace impurities, delivering hydrogen at purities of 99.97% or higher. The PSA offgas, still containing valuable hydrogen and combustible components, is often recycled as fuel for the cracking furnace, further enhancing process efficiency.
FB Group’s modular approach to ammonia cracking
Ammonia cracking technology aligns exceptionally well with FB Group’s expertise in skid-mounted process units. The standardized nature of the cracking process-vaporization, catalytic reaction, heat recovery, and purification-makes it ideal for modular fabrication. FB Group designs and delivers these units as complete, pre-integrated skids that can be manufactured in controlled workshop environments, tested thoroughly before shipment, and rapidly deployed at customer sites worldwide.
This modular approach offers distinct advantages for project execution. Clients benefit from reduced on-site construction time, minimized weather-related delays, and improved quality control compared to traditional stick-built installations. For ammonia import terminals, hydrogen refueling stations, or industrial facilities requiring on-demand hydrogen supply, FB Group’s skid-mounted ammonia cracking units provide a turnkey solution that can be scaled according to specific capacity requirements-from 10 kg/h hydrogen for smaller applications to systems processing hundreds of kilograms per hour.
Strategic benefits for energy industry applications
Ammonia cracking units deliver compelling advantages across multiple energy sector applications. For refineries and chemical plants, these systems enable the replacement of conventional steam methane reforming hydrogen production with cleaner alternatives when fed with green or blue ammonia. The technology supports decarbonization initiatives while utilizing existing ammonia handling infrastructure.
In the maritime sector, ammonia cracking units facilitate the adoption of hydrogen fuel cells for vessels. Ships can carry ammonia-a liquid at modest pressure-and crack it on-board or at port facilities to generate hydrogen for propulsion systems. This approach circumvents the complex cryogenic storage requirements of pure hydrogen.
Remote and off-grid locations particularly benefit from this technology. Mining operations, island power systems, and isolated industrial sites can import ammonia via conventional logistics and produce hydrogen locally, avoiding the need for dedicated hydrogen pipelines or expensive local production facilities.
Enabling the hydrogen economy
Ammonia cracking units represent essential infrastructure in the emerging hydrogen economy. They effectively “unlock” hydrogen from its ammonia carrier, enabling a practical global hydrogen supply chain that leverages existing ammonia production, shipping, and storage capabilities. As countries and industries accelerate their energy transition strategies, the ability to efficiently convert ammonia to high-purity hydrogen at distributed locations becomes increasingly valuable.
For organizations seeking reliable, modular solutions to support hydrogen infrastructure development, ammonia cracking technology offers a proven pathway. Combined with expert process engineering and fabrication capabilities, these systems deliver the flexibility and performance required for tomorrow’s clean energy landscape.